“Every weekend I take an ATV out into the desert and spend a day tracing a faint “(C) GOOGLE 2009” watermark across the landscape.”
Be better if it was (C) GOOGLE 1995. Really f*** with their heads!
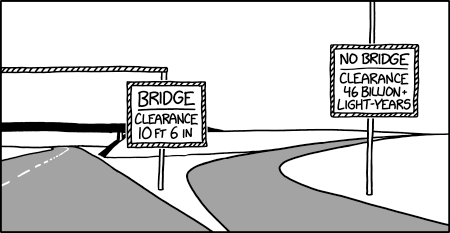
“A lot of the highway department’s budget goes to adjusting the sign whenever the moon passes directly overhead.”
So, this spot is no further than 28.5 degrees from the equator. And given the sign is in English with 'murrican units, that pretty much limits the location to somewhere in deep south Texas or Florida, I think. Oh, and Hawaii. Any American bases in that range?
Huh? Locations less poleward than ~23 degrees have an 1AU ~= 8 lightminute obstruction a couple times per day.
Did you mean a couple times per year?
Of course, there are lots of stars a lot closer than 46 billion light years that pass over every location on Earth once a day. And this reminds me of this older xkcd:
Nope. They each pass over a very narrow strip of latitude once a day. ETA: On rereading, I realize you meant they will collectively pass over every location. Yeah pretty much, especially if you count the stars in other galaxies.
There are some TNOs that have extreme inclinations, including a number that are in retrograde orbits. Some have orbits pretty close to perpendicular to the plane of the Solar System. Those will eventually pass over almost everywhere on Earth. Examples 2015 KZ120 has inclination of 84.49 degrees; 2016 FH13 has 93.57. There’s some others with similar inclinations. Source: List of known trans-Neptunian objects
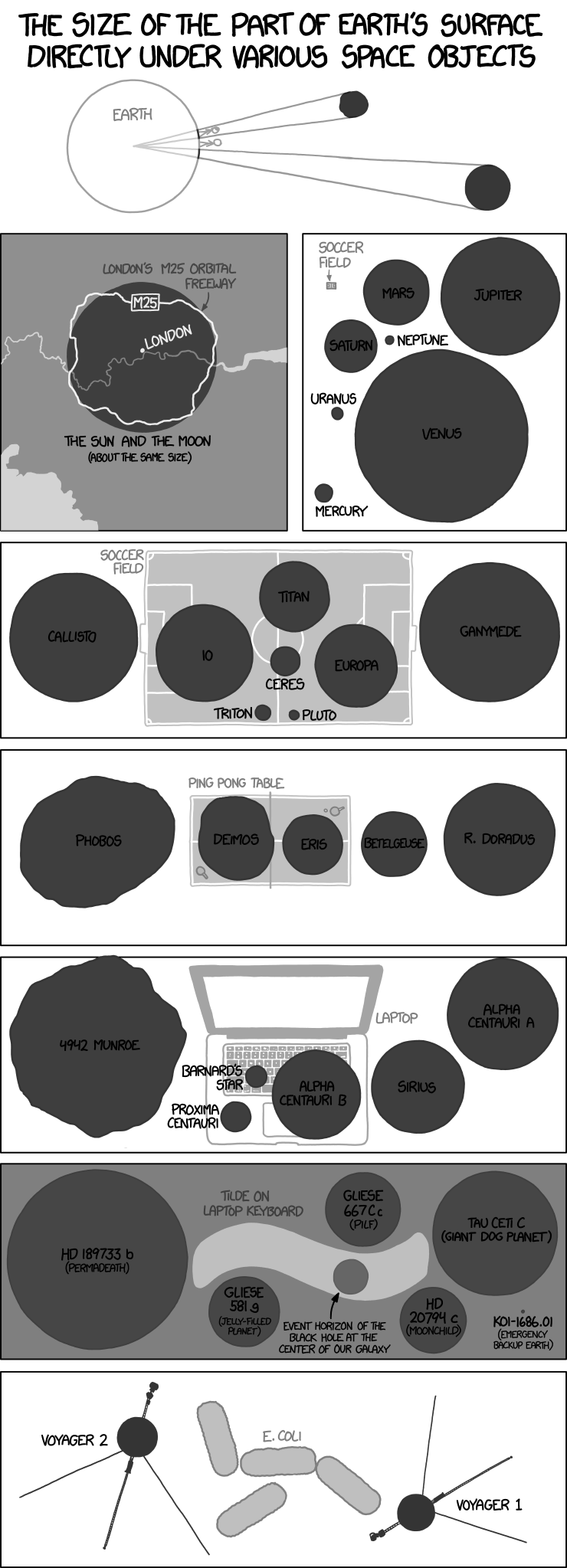
Not really. Note from your chart that even a star with a really large angular size only passes directly over an area about the size of a computer keyboard, and most stars are far, far smaller than that in the sky. Most places you could put a sign, no star would ever pass directly over them (though you’d have a lot of misses of less than a degree, but at stellar distances, that’s a big miss).
Mind. Blown.
(I knew about the moon and sun, from eclipse maps…but the rest amazes me. Though I shouldn’t have been too surprised about Venus, having taught myself about its transit across the sun…)
Which reminds me of Olber’s paradox…
Isaac Asimov wrote an essay “Heaven On Earth”, where he translated angular diameter to sizes on Earth’s surface; or as he put it, if the Earth was transparent and you viewed the sky from the Earth’s center.
Shouldn’t Venus and Mars be VERY variable in size depending on their opposition/ conjunction distances?
Yep. The max vs min distance ratio for both planets is very roughly 6.5 to 1. Which would lead to the same amount of variability of the shading diameter projected onto the Earth.
I have no idea what I meant. It was late, I was stupid. But yeah, “year” makes a lot more sense there. ![]()
What about starlink and other satellites? Depending on you location they could be overhead. Some briefly, and some geosynchronous ones all the time for certain locales.
Brian
All hogwash. The sky, sun, stars… are just projections shown to us flateathers. You sciency types just won’t acknowledge it. Even Munroe has been bought off by BIG DOME.
You’re not supposed to talk about that. If you get disappeared, don’t say I didn’t warn you.
But there’s lots more stars than what even the best telescopes can see. Gaia has mapped something like 2 billion stars and that’s only about 1% of the stars in our galaxy. Well, OK the stars in our galaxy are concentrated in a relatively narrow band. There won’t be nearly as many in the rest of the sky. But there’s zillions of other galaxies out there and they aren’t concentrated. Consider the Hubble Deep Field and other deep field. Those show that even in areas of the sky that are seemingly bare, there’s lots of very distant galaies filling in those gaps.
There needs to be a sign warning of low-flying aircraft under 40,000 feet. Maybe a lot lower!
At what point would the angular size correspond to a footprint smaller than the Planck length?
ETA: my rough guesstimate based on the Planck length and the radius of the Earth is that something would have to be 1042 times as far away as it is wide to appear that small. Since there are fewer than 1016 meters in a light year, that would have to mean “very small and very far away”.